Logical fallacies and discourse
In a previous post, I discussed holding controversial conversations about current events in the classroom. As an extension of that topic, I’m sharing some ideas and resources about a challenge common in public debate, commentary and social media: the use of logical fallacies.
Just what are logical fallacies? The Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL, one of my favorite resources) describes them as “common errors in reasoning that will undermine the logic of your argument. Fallacies can be either illegitimate arguments or irrelevant points and are often identified because they lack evidence that supports their claim.” Examples include:
- Ad hominem: An attack on the person making an argument, rather than on the argument itself.
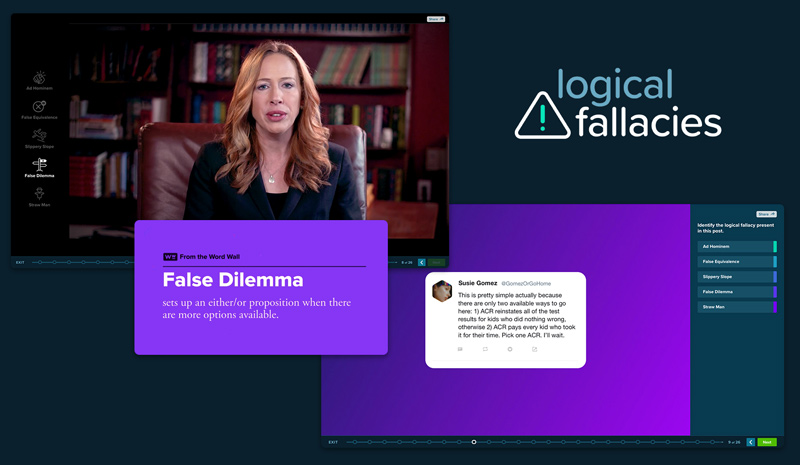
- False dilemma: An argument suggesting that only two options exist, when in fact there are more. Also called the “either/or,” “false choice” or “black and white” fallacy.
- False equivalence: Opposing arguments falsely made to appear as if they are equal.
- Slippery slope: An argument suggesting that a course of action, starting from a simple premise, will lead to disastrous results.
- Argumentum ad populum: An argument believed to be sound and true because it is popular. Usually referred to as “the bandwagon.”
In today’s social media world of character limits, memes and overflowing feeds, it’s increasingly difficult to convey a persuasive argument that is supported by evidence — and it’s really easy to share a short blast of opinion with a logical fallacy at its center. Those sorts of posts are notable specifically for their lack of credible evidence to support a claim or an argument, with fallacious reasoning used to fill the gaps. Here’s an example:
We must stop kids from playing video games. You buy them a game system and it’s only a matter of time before they’ll be fat and lazy, never leaving your basement. Parents all over this country agree that video games have no value whatsoever. We must either ban video games entirely for kids under the age of 16 or prepare for a generation of high school dropouts. The makers of these gaming systems are clearly greedy, manipulative predators out to keep our children addicted to their screens.
As young people engage in conversations about political, social or cultural issues, they need to be able to recognize logical fallacies — not just when others use them, but when they’re framing their own arguments. The ability to closely evaluate claims and arguments is a key element of critical thinking.
In “Arguments & Evidence” — a new lesson in our Checkology® virtual classroom — we discuss five of the most common types of logical fallacies. In developing that lesson, I researched resources for evaluating arguments and spotting logical fallacies. These are among the ones that I found most informative; they provide definitions, examples and context:
- “Monty Python and the Quest for a Perfect Fallacy”: This comprehensive lesson plan was developed by the Annenberg Classroom, a project of the Leonore Annenberg Institute for Civics at the University of Pennsylvania’s Annenberg Public Policy Center. It includes definitions, examples and reproducible materials for students.
- “Thou Shalt Not Commit Logical Fallacies”: This site was developed by The School of Thought International, a nonprofit that develops education resources on “critical thinking, creative thinking, and philosophy.” It has flashcards and posters — available both for purchase and as free PDF downloads — that integrate logical fallacies as part of critical-thinking exercises.
- An Illustrated Book of Bad Arguments: This free online book by Ali Almossawi, an engineer at Apple who writes about both critical thinking and computer science, contains wonderful illustrations and explanations for logical fallacies.
- Rational Wiki: “Logical fallacy”: Rational Wiki is owned and operated by the RationalMedia Foundation, a nonprofit whose mission “is to promote and defend science, critical thinking and public interest dialog in a free and open forum.” This comprehensive article offers great examples of logical fallacies focusing on science, statistics and studies.
- “18 Common Logical Fallacies and Persuasion Techniques”: In this Psychology Today article, Christopher Dwyer, a post-doctoral researcher in psychology at the National University of Ireland, describes “18 forms of persuasion techniques, illogical argumentation and fallacious reasoning” commonly encountered in social media.
- “Spot the Flaw in a Politician’s Argument With This Guide to Logical Fallacies”: This guide from Lifehacker focuses on fallacies used by politicians.
If you have a go-to resource for teaching logical fallacies, or another suggestion for incorporating such lessons into the classroom, please share it with me (Twitter: @MrSilva; email: [email protected])!
