Rumor Review
Misinformation creates coronavirus ‘infodemic’
Here are just two recent examples of the coronavirus ‘infodemic’ related to the outbreak:
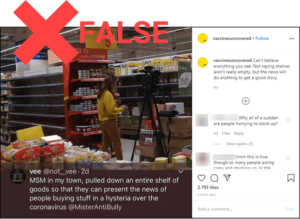
Panic buying not staged by media
NO: A mainstream media (MSM) news outlet did not stage evidence of COVID-19 panic by removing goods from shelves in a grocery store. YES: The Romanian TV news program Observator did use video of empty store shelves and coolers in a report on Feb. 26 about people buying large quantities of specific items to prepare for a possible outbreak of the disease. These include flour, canned goods and water. YES: The photo in the post above was taken during a live report broadcast the next day. The news channel whose reporter appears in the photo above has debunked this claim.
Escape from quarantine post a hoax
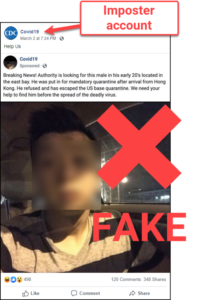
NO: A man in his early 20s did not escape from a mandatory COVID-19 quarantine on a U.S. military base. NO: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) did not run this Facebook ad about this nonexistent “escapee.” YES: This ad (note the word “Sponsored”) was purchased by an imposter page named “Covid19” and using the CDC logo.
WHO describes a coronavirus ‘infodemic’
There is far more misinformation about COVID-19 and the strain of coronavirus that causes it than we can adequately address here. For additional coverage of what the World Health Organization has called an “infodemic,” see:
- “Here’s A Running List Of The Latest Disinformation Spreading About The Coronavirus” (Jane Lytvynenko, BuzzFeed News).
- “Surge of Virus Misinformation Stumps Facebook and Twitter” (Sheera Frenkel, Davey Alba and Raymond Zhong, The New York Times).
- “In Facebook groups, coronavirus misinformation thrives despite broader crackdown” (Brandy Zadrozny, NBC News).
Questions for discussion in the classroom
Why do you think rumors like this have appeal? What journalism standards and ethic policies address the authenticity of photos and video footage?